
By Milton Kirby | Atlanta, GA | March 6, 2025
One of the most significant legal battles in American history unfolded in St. Louis’ Old Courthouse, where Dred Scott and his wife, Harriet, fought for their freedom from enslavement. The landmark Supreme Court decision in Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857) not only denied their freedom but also ruled that African Americans could not be U.S. citizens and that Congress had no authority to prohibit slavery in federal territories. This ruling invalidated the Missouri Compromise of 1820 and pushed the nation closer to the Civil War.
Dred Scott’s Journey to the Courtroom
Dred Scott was born into enslavement in Virginia around 1799 and later moved with his enslavers, the Blow family, to St. Louis in 1830. Financial difficulties forced the Blows to sell Scott to Dr. John Emerson, a military surgeon. Scott accompanied Emerson to free territories—Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory—where slavery was prohibited under the Missouri Compromise.
During this time, Scott married Harriet Robinson, who was also enslaved. The couple had two daughters, Eliza and Lizzie. After Dr. Emerson died in 1843, his widow, Irene Emerson, continued to profit from their forced labor, hiring them out to other families.
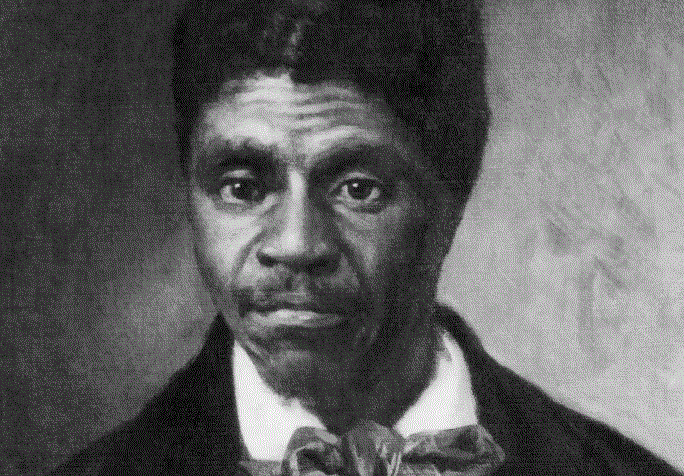
In 1846, Scott took legal action, suing Irene Emerson for his freedom. The case, filed in the Old Courthouse, was based on the legal precedent that an enslaved person who had lived in a free territory was entitled to freedom. With the support of abolitionist allies and financial backing from the Blow family, Scott embarked on an eleven-year legal battle that would reach the highest Court in the land.
The Supreme Court’s Ruling and Its Fallout
On March 6, 1857, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled 7-2 against Scott. The Court, led by Chief Justice Roger B. Taney, declared that African Americans, whether free or enslaved, could not be U.S. citizens and therefore had no right to sue in Federal Court. Moreover, the ruling struck down the Missouri Compromise, stating that Congress had no power to prohibit slavery in U.S. territories.

Taney actually freed the enslaved people that he had inherited; however, he believed that the Federal government had no right to limit slavery. He mistakenly thought he could save the Union when he ruled that the Framers of the Constitution believed enslaved people were so inferior that they possessed no legal rights.
Chief Justice Taney held the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional, claiming that as property, enslaved people were protected under Article V. In addition to this unpopular opinion, Taney became even more disliked when he challenged President Lincoln’s constitutional authority to apply certain emergency measures during the Civil War. Lincoln saw him as an enemy and even defied one of Taney’s judicial decisions. Despite his critics, Taney served until he died on October 12, 1864, at the age of 87, after being Chief Justice for 28 years.
This decision deepened the nation’s divide over slavery, further fueling tensions that would lead to the Civil War. Though Scott lost his case, his courage in seeking justice contributed to the broader movement for abolition.
The Missouri Compromise and Its Repeal
Scott’s case directly challenged the Missouri Compromise (also known as the Compromise of 1820) which was, Federal legislation of the United States that balanced northern states’ desires to prevent slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state and declared a policy of prohibiting slavery in the remaining Louisiana Purchase lands north of the 36th parallel. The 16th United States Congress passed the legislation on March 3, 1820, and President James Monroe signed it into law on March 6, 1820.
The Missouri Compromise was a critical effort to prevent the nation from fracturing over slavery, but it was repealed in 1854 by the Kansas-Nebraska Act, which allowed territories to decide the issue of slavery through popular sovereignty. The Supreme Court’s ruling in Dred Scott v. Sandford further dismantled any legal barriers to slavery’s expansion, emboldening pro-slavery factions and enraging abolitionists.
Legacy of the Dred Scott Case
Though the Supreme Court denied Scott’s plea for freedom, his case became a turning point in American history. The ruling heightened national tensions and galvanized anti-slavery forces, accelerating the path to the American Civil War. In 1857, Scott and his family were eventually freed by Taylor Blow, a member of his original enslaver’s family. Tragically, Scott died just a year later.
Dred and Harriet Scott’s determination to fight for their freedom stands as a testament to the resilience of those who resisted enslavement. Their struggle helped shape the national debate over slavery and ultimately contributed to the Union’s commitment to ending the institution once and for all.
The Union won the American Civil War. The war effectively ended in April 1865 when Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered his troops to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House in Virginia.









That was a great history lesson?
Doing the research for this project was a remarkable reminder of the struggle for freedom that our ancestors endured and the continuing struggle that the current generation still faces. The lack of freedom is sometimes less obvious but still ever-present.
Thank you for your continued support or our work.